Read the related story, “Concrete, Steel, or Wood: Searching for Zero-Net-Carbon Structural Materials.”
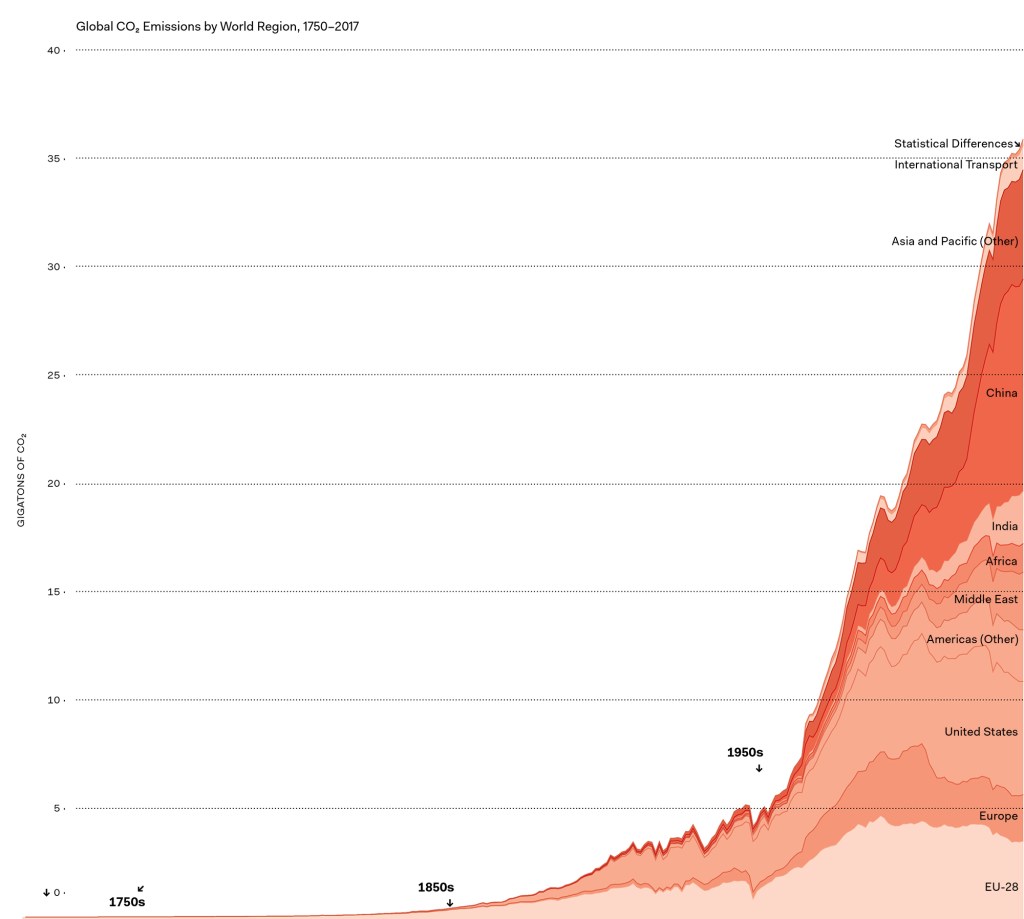
Measuring embodied carbon is complicated. It requires tracking materials through fantastically elaborate manufacturing supply chains. With so many variables, “the precision of a great deal of ecodata is low,” writes British materials scientist Michael Ashby in his book Materials and the Environment (Butterworth-Heinemann, 2009).
The good news is that more manufacturers and industry groups are publishing environmental impact data on their products, often with third-party verification. Even better, new digital tools make it possible to compare life cycle analyses (LCAs) and Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) during the course of project development. Examples include:
- LCA Practice Guide by the Carbon Leadership Forum
- Athena Sustainable Materials Institute’s Impact Estimator
- Tally for Revit application by KieranTimberlake
- Beacon for Revit by Thornton Tomasetti
- Embodied Carbon in Construction Calculator (EC3) by the Carbon Leadership Forum
- One Click LCA by Bionova
- Architecture 2030 Carbon Smart Materials Palette
- AIA Framework for Design Excellence

Source: EPD International
Sample Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) template
The change is welcome. EPDs to date have proven woefully incomparable. Though all EPDs conform to the same ISO standard, each one defines its own product category rules and presents its data in a different format. Many EPDs even come with a disclaimer renouncing their comparability. For example, you may be able to search for products with the lowest global warming potential, but the underlying data may reflect only a portion a product’s life cycle: the pre-construction phase (known as “cradle to gate”); a limited portion of the manufacturing phase (“gate to gate”); or the entire life cycle (“cradle to grave”), including maintenance and end of life.
The most useful EPDs are not only verified by a third party, such as UL, but also include data on specific manufacturers and factories. Industry-average data may conceal wide swings in the carbon footprints of different manufacturers and regional supply chains.
The takeaway? Always ask for cradle to grave EPDs from manufacturers and leverage tools that allow for comparability.
This article appeared in the January 2020 issue of ARCHITECT, with the headline “Making Sense of the Metrics.” With additional reporting by Katharine Keane on the list of resources and tools.

-
The Carbon Issue
Meeting the urgent need for climate action, with decarbonization strategies for materials, design, practice, and policy.

-
It’s Time to Quit: A Call to Action on Climate, Carbon, and the Built Environment
Adapted from the opening and closing keynotes given by Edward Mazria, FAIA, at the CarbonPositive’19 Summit in Chicago.
-
The Language of Carbon
Thinking about COPY 27, here's a refresher of seventeen terms that will help you talk the talk of carbon positive design.

-
Sustainable Building Materials for Low Embodied Carbon
Here are eight of the most carbon-friendly products for roofing, cladding, insulation, and other categories—all of which are available for specification, or soon to be.

-
Concrete, Steel, or Wood: Searching for Zero-Net-Carbon Structural Materials
Steel and concrete predominate the U.S. commercial building market for structural materials, while engineered wood—specifically mass timber—is garnering attention for its potential embodied carbon savings and sequestration ability.

-
How to Measure Embodied Carbon
Here's a hand guide on some tips and tools to help determine the carbon footprint of a project or product.

-
Five Construction Details to Reduce Embodied and Operational Carbon
It's time to rethink details that perpetuate the widespread use of energy-intensive materials.

-
Renovation, Restoration, and Adaptive Reuse: The Understated Value of Existing Buildings
It’s not enough to design super-efficient new buildings. To reach zero-net carbon, architects have to improve performance in existing buildings, and make the most of the embodied carbon we’ve already spent on them.

-
With Housing’s Carbon Footprint, Density Matters
A new e-book from Chicago-based Adrian Smith + Gordon Gill Architecture analyzes the embodied carbon and other attributes of nine housing types to uncover ideal residential densities—those that improve quality of life while minimizing their environmental impact.
-
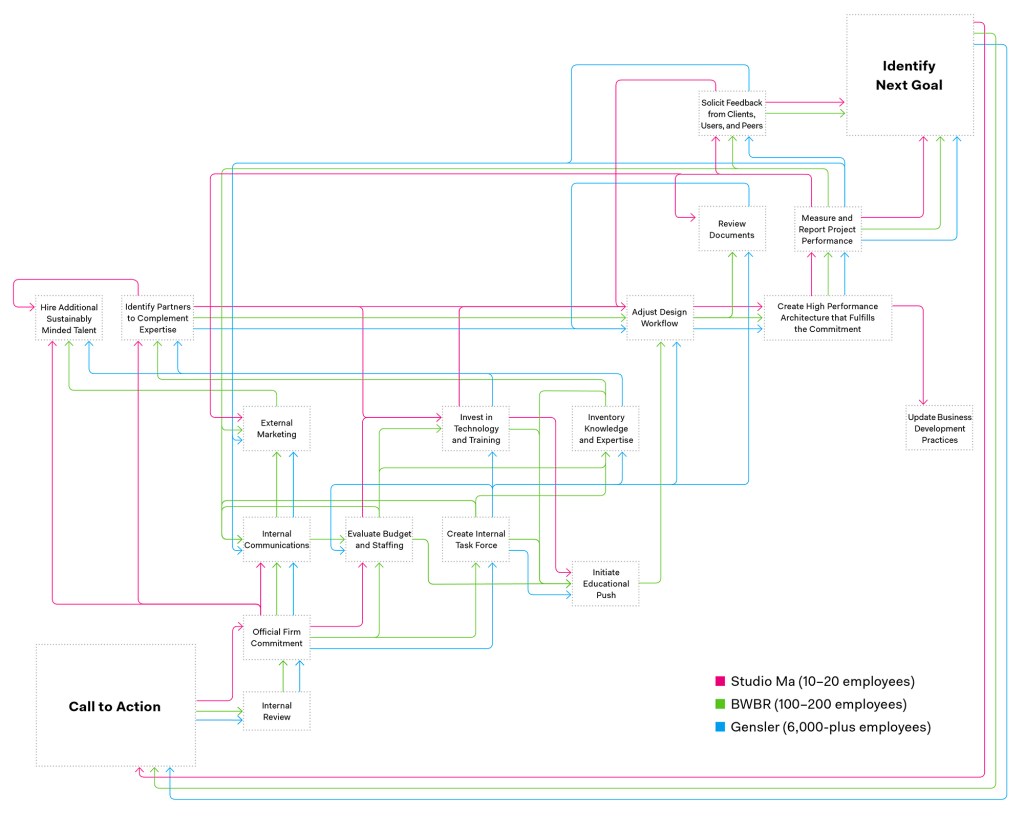
Aim Higher: How to Transition Your Firm to Zero Net Carbon
Looking for tangible steps to committing to zero-net-carbon design? Here, three very different practices—Studio Ma, BWBR, and Gensler—share their ongoing journeys.